BRANCHING/ DECISION
(IF ELSE / SWITCH CASE)
Three Main Construction of Programming :
1. Sequential
2. Branching / Decision
3. Looping / Repetition
Branching :
- A process to make a decision based on the condition which has been evaluated before.
There are two types of branching :
1. IF – ELSE
Syntax : if (condition){
statement – 1;
statement – n;
}
else if (condition){
statement – 1;
statement – n;
}
Flowchart :
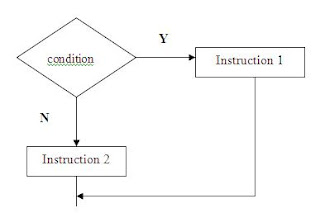
Example :
#include
#include
int main()
{
int T;
printf("Enter temperature (Celcius) : ");
scanf("%d",&T);
if (T>30)
{
printf("Arghhhhhhh, Hot!");
}
else if (T<0)
{
printf("Ouchhhhh, Cold !");
}
else printf("Yummy! Cool.");
getch();
return(0);
}
2. SWITCH – CASE
Syntax : switch (kondisi) {
case 1 : pernyataan-1;
break;
case 2 : pernyataan-2;
break;
.....
.....
case n : pernyataan-n;
break;
default : pernyataan-m
}
Flowchart :

Example :
#include
#include
int main()
{
char IP;
printf("Enter your result in alphabet : ");
scanf("%c",&IP);
switch (IP)
{
case 'A' : printf("4");
break;
case 'B' : printf("3");
break;
case 'C' : printf("2");
break;
case 'D' : printf("1");
break;
case 'E' : printf("0");
break;
default : printf("The input isn’t valid.");
}
getch();
return(0);
}
The difference between IF-ELSE and SWITCH-CASE :
IF ELSE :
To make a decision between 2 choices. For example :
If the value is greater than 70 (seventy) then the student passes the exam.
Else, the student doesn’t pass the exam.
SWITCH CASE :
To make a decision which has more than 2 choices. For example :
A is converted to 4.
B is converted to 3.
C is converted to 2.
D is converted to 1.
E is converted to 0.


0 comments:
Post a Comment